Algorithm
[알고리즘]SWEA_1954.달팽이숫자
이수밈
2023. 8. 12. 16:01
SW Expert Academy
SW 프로그래밍 역량 강화에 도움이 되는 다양한 학습 컨텐츠를 확인하세요!
swexpertacademy.com
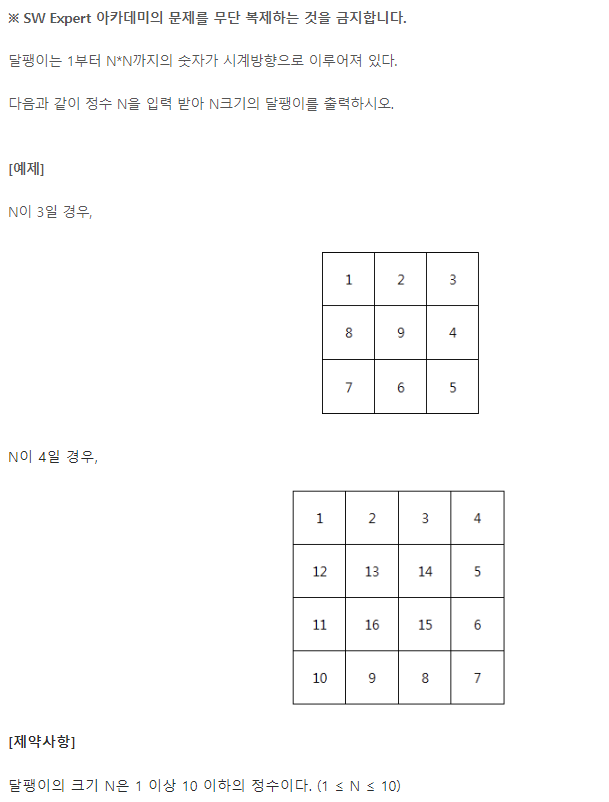

import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Swea_달팽이 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int T = sc.nextInt();
for (int tc = 1; tc <= T; tc++) {
int N = sc.nextInt();
int[][] snail = new int[N][N];
snail[0][0] = 1; // 시작점은 1에서부터 시작하니까.
int K = 2; // 입력시작하는 값은 2
int r = 0;
int c = 0;
while (K <= N * N) {
while (c < N - 1 && snail[r][c + 1] == 0) {
c++;
snail[r][c] = K++;
}
while (r < N - 1 && snail[r + 1][c] == 0) {
r++;
snail[r][c] = K++;
}
while (1 <= c && snail[r][c - 1] == 0) {
c--;
snail[r][c] = K++;
}
while (1 <= r && snail[r - 1][c] == 0) {
r--;
snail[r][c] = K++;
}
}
System.out.println("#" + tc );
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<N;j++) {
System.out.print(snail[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}- 출력은 1부터 되기 때문에 배열의 출력값을 1로 초기화해준다.
- 초기화 후에는 2부터 입력하기 때문에 K의 초기값을 2로 설정한다.
- 왼쪽에서 오른쪽으로 이동 : N-1번째 열보다 작으면서, 다음 배열값이 없을때까지 행방향 순회한다.
- 위에서 아래로 이동 : N-1번째 행보다 작으면서, 다음 배열값이 없을때까지 열방향으로 순회한다.
- 오른쪽에서 왼쪽으로 이동 : 첫번째 열까지 역순회하면서, 다음 배열값이 없을때까지 순회한다. 그때 c--!!!
- 아래에서 위로 이동 : 첫번째 행까지 역순회하면서, 다음 배열값이 없을때까지 순회한다. r-- 해주는 것이 포인트
- > 4로 나누었을 때 나머지를 이용하여 푸는 방법도 유용할 수 있음. 공부해보쟈~~
8/13 : 4로 나누었을 때 나머지를 이용하여 푸는 방법도 공부했다.
public class Snail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 5;
int arr[][] = new int [10][10];
//입력된 n*2-1만큼 이동
int x = 0;
int y = 0; //배열의 좌표
int num = 1;
int f = n; //한방향으로 가는 숫자의 개수..
for(int i=0;i<2*n-1;i++) {
switch(i % 4) {
case 0: //right way
for(int k=0;k<f;k++) {
arr[y][x] = num;
x++;
num++;
}
x--;
y++;
f--;
break;
case 1: //under way
for(int k=0;k<f;k++) {
arr[y][x] = num;
y++;
num++;
}
y--;
x--;
break;
case 2: //left way
for(int k=0;k<f;k++) {
arr[y][x] = num;
x--;
num++;
}
x++;
y--;
f--;
break;
case 3: //up way
for(int k=0;k<f;k++) {
arr[y][x] = num;
y--;
num++;
}
y++;
x++;
break;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<n;j++) {
System.out.printf("%3d", arr[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}